Steady Industrial Fasteners Co., Ltd.
Steady Industrial Fasteners Co., Ltd. is and , specialized in producing Blind Fasteners, including Rivet Nuts, Rivets, Clinching Fasteners and Welding Studs. With more than 10 years experience in production and exporting, STEADY is a High & New technology enterprise founded in 2001.
Wtih ISO 9001:2009, TS16949 certified facilities in Zhejiang, China. We can manufacture 1.5 billion blind rivets that meet DIN7337, IFI and GB(chinese) standards annually, Plus 283 million pieces rivet nuts 120 million pieces of clinching fasteners annually, that most competitors can not simply compete.

Honor
a professional manufacturer of blind fasteners.
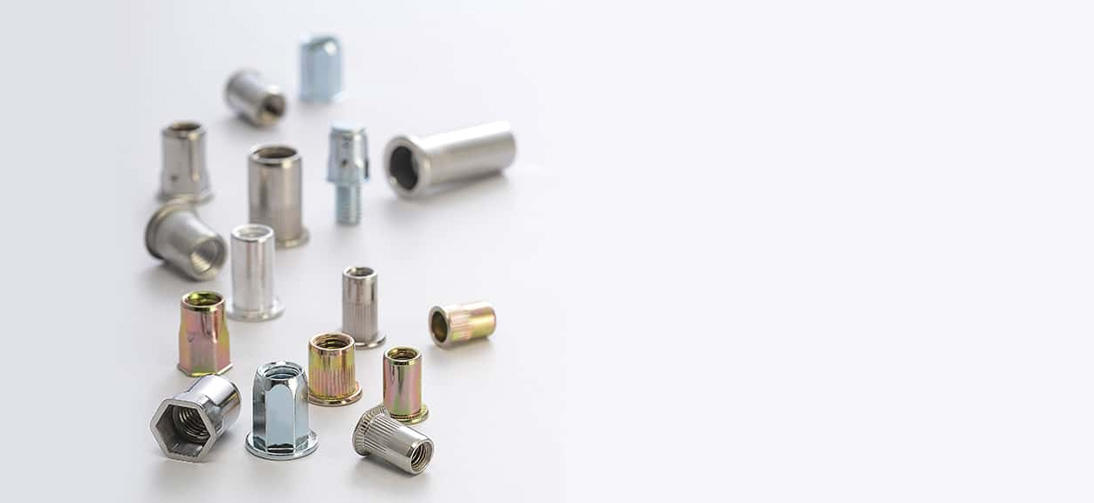
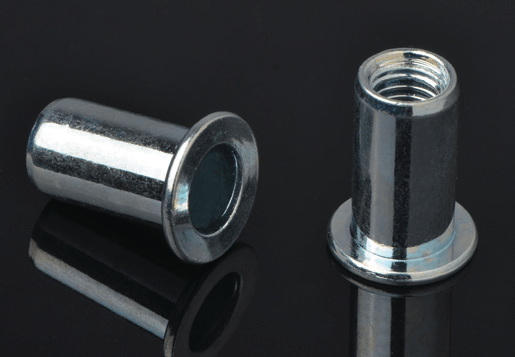
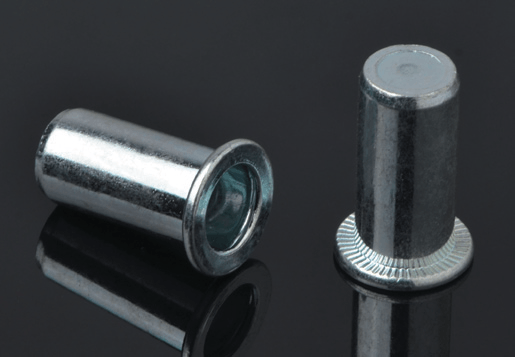
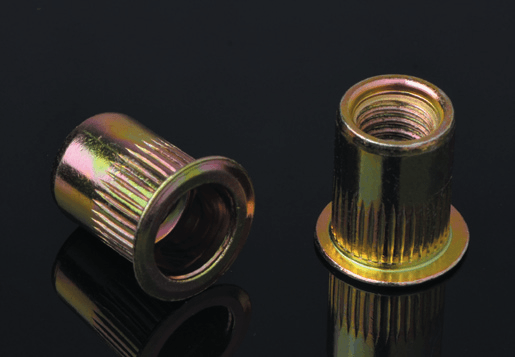
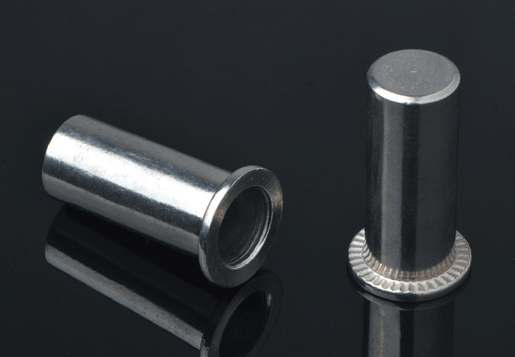
STEADY manufactures over thousands different type of blind rivet nuts in steel,aluminium and stainless steel, diameter from M3-M16 in metric and UNC #6-32 to UNC 1/2-13 in inch. High advantage in stainless steel blind rivets both for open and sealed type, mutigrip,monobolt and other structural rivets. We focus on "one stop shopping" and with advantage of large production capacity , consistent quality, competitive prices, punctual delivery and excellent serverices before and after sales, STEADY has become one of the leading blind fasteners manufacuture & supplier in Asia.


Latest news
-
Industry news
Are rivnuts stronger than screws?
When it comes to fastening materials, engineers and fabricators often face a critical choice: rivnuts or screws? While both serve to join components, ...
14th Jul,2025 -
Industry news
How Do You Use a Blind Rivet Nut?
Blind rivet nuts, often simply called rivet nuts or threaded inserts, are versatile fasteners used to create a threaded hole in materials where tappin...
08th Jul,2025 -
Industry news
How to install self-clinching fasteners?
Self-clinching fasteners are a popular choice in manufacturing and engineering for creating strong, permanent threads in thin sheet metal. Unlike trad...
01th Jul,2025 -
Industry news
Weld-Studs: A Key Component in Structural and Industrial Fastening
Weld-studs are essential mechanical fasteners used across various industries, including construction, shipbuilding, automotive, and manufacturing. The...
23th Jun,2025 -
Industry news
Are Rivet Nuts Permanent?
Rivet nuts—also known as rivnuts or threaded inserts—are increasingly popular in industries such as automotive manufacturing, aerospace, furniture pro...
17th Jun,2025


 EN
EN  英语
英语 俄语
俄语 韩语
韩语 阿拉伯语
阿拉伯语 土耳其语
土耳其语








 +(86)-133 8863 9264
+(86)-133 8863 9264